Galaxy s7 secure folder with android 7 0 update – Galaxy S7 Secure Folder with Android 7.0 update: Remember those paranoid days before password managers? This deep dive explores Samsung’s Secure Folder feature on the Galaxy S7 after the Android 7.0 upgrade, dissecting its security, ease of use, and how it stacks up against other Android versions. We’ll uncover its strengths, weaknesses, and whether it was truly the fortress of digital privacy it promised to be.
From encryption methods to real-world use cases (think hiding those embarrassing vacation pics!), we’ll walk you through setting up your own secure space and address common user concerns. We’ll also compare it to its performance on other Android versions and devices, offering a comprehensive look at this once-popular feature.
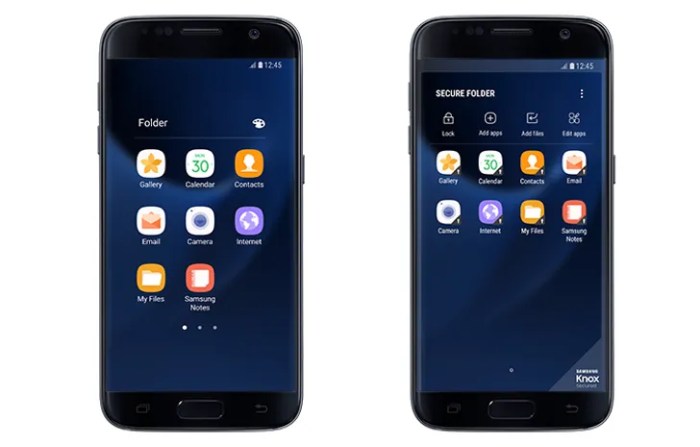
Secure Folder Functionality on Galaxy S7 with Android 7.0
The Samsung Secure Folder, introduced on the Galaxy S7 with the Android 7.0 Nougat update, offered a compelling solution for enhanced data privacy. It provided a separate, isolated space within the phone’s storage, adding an extra layer of security beyond the standard Android encryption. This feature allowed users to compartmentalize sensitive information, keeping it separate from their main profile.
Secure Folder Features and Limitations on Galaxy S7 with Android 7.0
The Secure Folder on the Galaxy S7 running Android 7.0 allowed users to store various types of data, including apps, photos, videos, documents, and contacts. However, it’s crucial to understand that while Secure Folder offered enhanced security, it wasn’t impenetrable. The level of security depended heavily on the user’s password strength and adherence to best practices. Limitations included the inability to share files directly from the Secure Folder to external apps without first moving them to the main storage. Additionally, if the device was compromised through other vulnerabilities, access to the Secure Folder might still be possible.
Encryption Methods Employed by Secure Folder on Android 7.0, Galaxy s7 secure folder with android 7 0 update
While Samsung didn’t publicly detail the precise algorithms used in Secure Folder encryption on Android 7.0, it’s safe to assume it relied on a combination of hardware-backed security features (like the Knox security platform) and software-based encryption. The data within the Secure Folder was isolated and encrypted, making it inaccessible without the correct authentication. This likely involved AES encryption, a widely used and robust standard for data protection. The exact implementation, however, remained proprietary information.
Data Types Supported Within the Secure Folder
The Secure Folder on the Galaxy S7 with Android 7.0 supported a range of data types. Users could securely store apps (duplicating apps from the main profile), photos, videos, documents (various file formats), and contacts. This allowed for a significant level of data segregation, ensuring that sensitive personal or professional information remained isolated from the main phone storage.
Comparison of Secure Folder Security to Other Android 7.0 Data Protection Methods
Compared to other data protection methods available on Android 7.0, the Secure Folder offered a more user-friendly and integrated approach. While Android 7.0 had built-in encryption for the entire device, the Secure Folder provided granular control, allowing users to choose which specific data to protect. This differed from simply relying on a strong device password or third-party encryption apps, which often lacked the seamless integration offered by the Secure Folder.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up and Using the Secure Folder
Setting up and using the Secure Folder was relatively straightforward. The following table Artikels the process:
| Step Number | Action | Description | Screenshot Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Locate Secure Folder | Find the Secure Folder app in the app drawer. | A screenshot showing the app drawer with the Secure Folder icon highlighted. The icon might be a folder with a lock on it. |
| 2 | Create Secure Folder | Tap the Secure Folder app to launch it and follow the on-screen prompts to create the folder. This will likely involve setting a PIN, pattern, or password. | A screenshot showing the initial setup screen, possibly with options for password type selection. |
| 3 | Add Data | Once created, you can add apps, files, or contacts to the Secure Folder. | A screenshot showcasing the Secure Folder interface with options to add apps, files, or contacts. |
| 4 | Access Secure Folder | Access the Secure Folder using the app or the dedicated widget (if added to the home screen). You’ll need to authenticate with your chosen password, PIN, or pattern. | A screenshot showing the Secure Folder access screen, requiring password/PIN/pattern entry. |
Security Implications of the Android 7.0 Update on Galaxy S7 Secure Folder: Galaxy S7 Secure Folder With Android 7 0 Update
The Android 7.0 Nougat update brought significant changes to the Samsung Galaxy S7, including refinements to its Secure Folder feature. While generally enhancing the overall device security, the update also introduced some nuances that warrant examination regarding potential vulnerabilities and strengthened defenses within the Secure Folder environment. Understanding these changes is crucial for users to maintain optimal data protection.
The update’s impact on Secure Folder security is multifaceted. It’s not simply a case of improvement or degradation; rather, it’s a shift in the security landscape requiring a reassessment of potential threats and mitigation strategies. Android 7.0 introduced improvements in core Android security, which indirectly benefited Secure Folder, but it also presented new attack surfaces that needed addressing.
Enhanced Encryption and Kernel Security
Android 7.0 implemented stronger encryption protocols and improved kernel security measures. This directly impacted the Secure Folder by bolstering the encryption protecting the data stored within. The improved kernel security reduced the likelihood of exploits gaining root access, thereby limiting potential attacks that could compromise the Secure Folder’s isolation. The enhanced encryption made brute-force attacks significantly more difficult, increasing the time and resources needed to crack the encryption key protecting the Secure Folder’s contents.
Potential Vulnerabilities Related to App Permissions
While Android 7.0 strengthened overall security, some vulnerabilities related to app permissions remained a concern. Malicious apps, even if they couldn’t directly access the Secure Folder, could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in other system apps to indirectly gather information or compromise device security. This could potentially affect the Secure Folder’s integrity indirectly, for example by creating a backdoor to other parts of the device which then might compromise the Secure Folder. This is particularly relevant if a malicious app gains access to system logs or processes which might reveal information about the Secure Folder’s activity.
Comparison of Secure Folder Security Before and After Android 7.0 Update
Before the Android 7.0 update, the Secure Folder relied on a combination of Knox and Android’s built-in security features. While effective, it was potentially more susceptible to exploits targeting specific vulnerabilities within the older Android version. After the update, the Secure Folder benefited from improved encryption, kernel security, and the overall security enhancements introduced by Android 7.0. However, the reliance on the overall device security meant that any vulnerabilities outside the Secure Folder could indirectly weaken its protection.
Hypothetical Security Breach Scenario and Mitigation
Imagine a scenario where a user installs a seemingly innocuous app that secretly contains malware. This malware, while not having direct access to the Secure Folder, exploits a vulnerability in another app to gain access to system logs. These logs might indirectly reveal the existence and activity of the Secure Folder, potentially providing information to a sophisticated attacker about the types of files stored within. This doesn’t directly compromise the Secure Folder’s encryption, but it provides valuable reconnaissance information. Mitigation involves being extremely cautious about app permissions, regularly updating the device and apps, and using a strong, unique password for the Secure Folder. Furthermore, regularly reviewing the device’s security logs for any suspicious activity can help in early detection of a potential breach.
Comparison with Other Android Versions and Devices
The Samsung Galaxy S7’s Secure Folder, while innovative for its time, wasn’t a standalone feature. Its functionality and security measures evolved alongside Android updates and across different Samsung devices. Understanding these changes provides valuable context to appreciate its strengths and limitations on Android 7.0. Comparing it with later iterations highlights advancements in security protocols and feature enhancements.
The Secure Folder’s evolution reveals a fascinating trajectory in mobile security. Early implementations focused on basic data isolation, while later versions incorporated more sophisticated encryption and integration with other Samsung services. This comparison will examine key differences in feature sets and security protocols across various Android versions and Samsung devices, specifically focusing on how the Android 7.0 implementation on the Galaxy S7 stacks up against its successors.
Secure Folder Feature Comparison Across Android Versions
This table compares Secure Folder features across Android 7.0 (Nougat), Android 8.0 (Oreo), and Android 9.0 (Pie) on a hypothetical Samsung Galaxy device. Note that specific features and security protocols might vary slightly depending on the exact device model and Samsung’s software customizations.
| Android Version | Feature Availability | Security Protocol | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android 7.0 (Nougat) | Basic file and app isolation; limited app compatibility. | Likely utilized Samsung Knox’s containerization technology, with encryption based on the Android 7.0 security framework. | More basic compared to later versions. Integration with other Samsung services was less extensive. |
| Android 8.0 (Oreo) | Improved app compatibility; potential for enhanced integration with other Samsung apps (e.g., Samsung Notes, Gallery). Possibly introduced support for more file types. | Likely leveraged advancements in Android’s encryption capabilities and potentially incorporated enhancements within Samsung Knox. | Significant improvements in both functionality and security compared to Android 7.0. |
| Android 9.0 (Pie) | Further refined app compatibility; potentially included features like biometric authentication improvements (fingerprint, face recognition) for Secure Folder access. | Enhanced encryption methods aligned with Android 9.0 security standards. Further refinement of Samsung Knox integration. | Built upon the improvements of Android 8.0, offering a more robust and feature-rich Secure Folder experience. |
Security Protocol Evolution in Secure Folder
The security protocols employed by Secure Folder evolved considerably across different Android versions. While Android 7.0 relied on the then-current encryption standards and Samsung Knox’s containerization technology, later versions benefited from advancements in Android’s security architecture and refinements within Samsung’s own security platform. For example, the introduction of more robust encryption algorithms and improved key management systems significantly enhanced the security of data stored within Secure Folder. Additionally, tighter integration with biometric authentication systems provided an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. These improvements are not merely incremental; they represent a substantial leap in protecting sensitive user data.
Ultimately, the Galaxy S7’s Secure Folder with Android 7.0 offered a decent layer of security for its time, but like all tech, it had its limitations. Understanding its capabilities – and its vulnerabilities – is key to making informed choices about your digital privacy. While newer Android versions boast enhanced security features, this exploration highlights the evolution of mobile security and the ongoing need for users to stay informed and proactive.
The Galaxy S7’s Secure Folder, enhanced with the Android 7.0 update, offered a serious boost to privacy. It’s interesting to compare that level of security to the specs of a more budget-friendly phone like the samsung galaxy j1 gets official with quad core cpu , which, while lacking similar security features, still represented a solid step up in processing power for its time.
Ultimately, the S7’s Secure Folder remains a standout feature, especially considering its integration with Android 7.0.
 Insurfin Berita Teknologi Terbaru
Insurfin Berita Teknologi Terbaru